Introduction
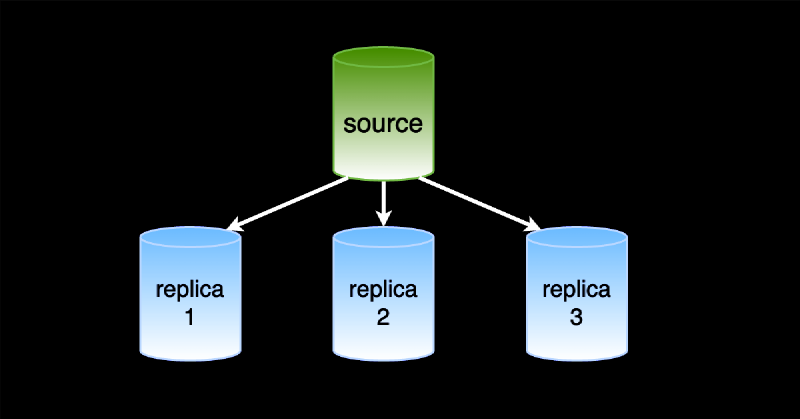
In this article, we will create a MySQL replica database. A MySQL replica is a read-only copy of the primary database, which is kept in sync with the main database using MySQL replication threads.
The steps we will follow are:
- Spin up MySQL source and replica databases
- Create a user for replication
- Obtain source binary log coordinates
- Configure replica DB and start replication
To add a replica to an existing MySQL database, see the copy database from source and start replication manually section.
Terminology: master-slave vs source-replica
In database replication, the terms master-slave and source-replica are used interchangeably. In recent MySQL versions, the term source-replica is preferred over master-slave due to its more neutral connotation. Many keywords and variables in MySQL have recently been renamed to use neutral terms. We will use the terms source and replica in this article.
What is database replication?
Database replication is a process that allows data from one database server (the source) to be copied to one or more database servers (replicas). Replication is asynchronous, meaning the replica instance does not need to be connected to the source constantly. The replica can catch up with the source when either becomes available.
Database replicas are used for:
- Scaling read operations
- High availability
- Disaster recovery
MySQL implements replication using the binary log. The source server writes changes to the binary log, and the replica server reads it and applies the changes to its database.
Create MySQL source and replica databases
We will use Docker to create the MySQL source and replica databases. We will use the
official MySQL Docker image. The source database will run on port 3308, and the
replica database will run on port 3309. Both servers will have the database named test. We tested these instructions
on MySQL 8.0.36, MySQL 8.4.3, and MySQL 9.1.0.
We run docker compose up using the following docker-compose.yml file:
Create a DB user for replication
Replication in MySQL requires a user with the
REPLICATION SLAVE
privilege. We will create a user named replicator with the password rotacilper.
Connect to the source database using the MySQL client:
mysql --host 127.0.0.1 --port 3308 -uroot -ptoor
Create the replicator user and grant the REPLICATION SLAVE privilege:
CREATE USER 'replicator'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'rotacilper';
GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'replicator'@'%';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Retrieve source binary log coordinates
For the replica server to start replication, it needs to know the source’s binary log file and position. We can obtain this information using the MySQL client we opened in the previous step.
SHOW BINARY LOG STATUS;
In MySQL 8.0, use the SHOW MASTER STATUS command instead of SHOW BINARY LOG STATUS.
The output will look like this:
+------------+----------+--------------+------------------+-------------------+
| File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | Executed_Gtid_Set |
+------------+----------+--------------+------------------+-------------------+
| bin.000003 | 862 | | | |
+------------+----------+--------------+------------------+-------------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
We must remember the File and Position values for the next step.
Configure replica DB and start replication
Now, we will connect to the replica database and configure it to replicate from the source database.
mysql --host 127.0.0.1 --port 3309 -uroot -ptoor
Use the CHANGE REPLICATION SOURCE TO command to configure the replica to replicate from the source. Replace
SOURCE_LOG_FILE and SOURCE_LOG_POS with the values obtained in the previous step.
CHANGE REPLICATION SOURCE TO
SOURCE_HOST='mysql_source',
SOURCE_PORT=3306,
SOURCE_USER='replicator',
SOURCE_PASSWORD='rotacilper',
SOURCE_LOG_FILE='bin.000003',
SOURCE_LOG_POS=862,
GET_SOURCE_PUBLIC_KEY=1;
SOURCE_HOST is the primary source’s hostname, which matches the docker service name. The GET_SOURCE_PUBLIC_KEY
option is needed for caching_sha2_password authentication.
Finally, start the replica:
START REPLICA;
The replica will now start cloning data from the source database. You can check the replication status using the
SHOW REPLICA STATUS\G command. Use this command to check for errors if you suspect something is wrong.
We can create a table with data on the source database and check if it is replicated to the replica database:
USE test;
CREATE TABLE users (id INT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(255));
INSERT INTO users VALUES (1, 'Alice');
Restore replication after an issue
If the replica crashes and comes back up, it may be unable to resume replication from where it left off. If the replica stops replicating due to an error, first try to restart replication on the replica:
STOP REPLICA;
START REPLICA;
Check the replication status for errors using the SHOW REPLICA STATUS\G command.
If the replica still does not replicate, we need to copy the database from the source and restart replication manually.
Copy database from source and start replication manually
Reset the replica:
STOP REPLICA;
RESET REPLICA ALL;
Optionally, drop and recreate the database on the replica:
DROP DATABASE test;
CREATE DATABASE test;
If the source database still has the binary log files around from the first time we set up replication, we can redo the original steps using the same source log file and position. If not, we need to back up the source database and restore it on the replica.
Backup the source database (on port 3308 with database name test):
bash -c 'mysqldump --host 127.0.0.1 --port 3308 -uroot -ptoor test | gzip -' > backup.sql.gz
Restore the backup on the replica database (on port 3309):
bash -c 'gzip -dc - | mysql --host 127.0.0.1 --port 3308 -uroot -ptoor test' < backup.sql.gz
Now, redo the following steps from above:
As you can see, restarting replication after an issue can be more involved than just restarting the replica. Regular backups can help in such situations. When backing up the source database, make sure to include the binary log files, along with the corresponding binary log position. You can then use these files to restore or spin up a new replica while the source database is actively running.
Further reading on database scaling
- Recently, we wrote about database gotchas when scaling applications. One of the issues we summarized was optimizing a MySQL INSERT with subqueries.
- In the past, we encountered a memory issue with MySQL prepared statements when scaling applications.
- We also wrote about securing your MySQL Docker container for Zero Trust.
Follow along with the MySQL source-replica video
Note: If you want to comment on this article, please do so on the YouTube video.