This article is part of a series on mTLS. Check out the previous articles:
What is Go?
Go is a statically typed, compiled programming language designed at Google. It is known for its simplicity, efficiency, and ease of use. Go is often used for building web servers, APIs, and command-line tools. We will use Go to make a client that uses mTLS.
Setting up the environment
We will use the same certificates and keys script from the mTLS with macOS keychain article. If you still need to generate the certificates and keys, please follow the instructions in that article.
In addition, we will import the generated certificates and keys into the macOS keychain. (In a future article, we will use the Windows Certificate Store instead.) Keeping private keys on the filesystem is insecure and not recommended. We aim to build an mTLS client fully integrated with the operating system’s keystore.
Finally, as in the mTLS Hello World article, we will use docker compose up to start two nginx servers:
- https://localhost:8888 for TLS
- https://localhost:8889 for mTLS
Building the TLS Go client
Below is a simple Go HTTP client.
package main
import (
"flag"
"fmt"
"io"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
urlPath := flag.String("url", "", "URL to make request to")
flag.Parse()
if *urlPath == "" {
log.Fatalf("URL to make request to is required")
}
client := http.Client{}
// Make a GET request to the URL
rsp, err := client.Get(*urlPath)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("error making get request: %v", err)
}
defer func() { _ = rsp.Body.Close() }()
// Read the response body
rspBytes, err := io.ReadAll(rsp.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("error reading response: %v", err)
}
// Print the response body
fmt.Printf("%s\n", string(rspBytes))
}
Trying the ordinary TLS server with:
go run client.go --url https://localhost:8888/hello-world.txt
Gives the expected result:
TLS Hello World!
The Go client is integrated with the system keystore out of the box.
However, when trying the mTLS server with the following:
go run client.go --url https://localhost:8889/hello-world.txt
We get the error:
<html>
<head><title>400 No required SSL certificate was sent</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>400 Bad Request</h1></center>
<center>No required SSL certificate was sent</center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.25.3</center>
</body>
</html>
The Go libraries are not integrated with the system keystore for using the mTLS client certificate and key.
Modifying the Go client for mTLS
We will use the crypto/tls package to build the mTLS client.
package main
import (
"crypto/tls"
"flag"
"fmt"
"io"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
urlPath := flag.String("url", "", "URL to make request to")
clientCert := flag.String("cert", "", "Client certificate file")
clientKey := flag.String("key", "", "Client key file")
flag.Parse()
if *urlPath == "" {
log.Fatalf("URL to make request to is required")
}
var certificate tls.Certificate
if *clientCert != "" && *clientKey != "" {
var err error
certificate, err = tls.LoadX509KeyPair(*clientCert, *clientKey)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("error loading client certificate: %v", err)
}
}
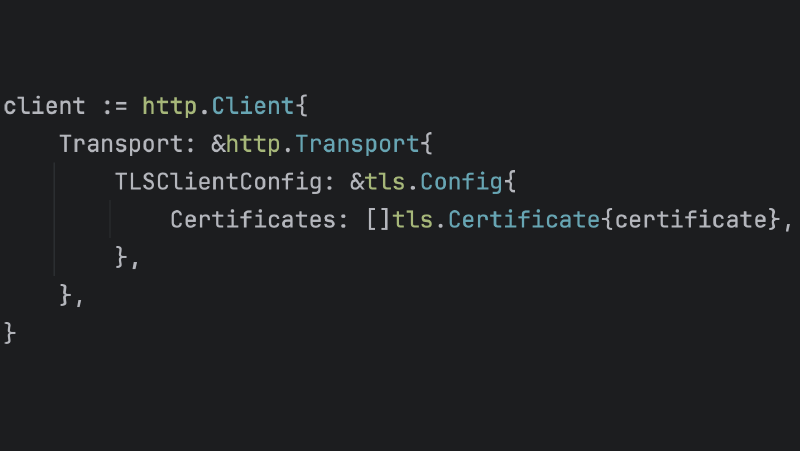
client := http.Client{
Transport: &http.Transport{
TLSClientConfig: &tls.Config{
Certificates: []tls.Certificate{certificate},
},
},
}
// Make a GET request to the URL
rsp, err := client.Get(*urlPath)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("error making get request: %v", err)
}
defer func() { _ = rsp.Body.Close() }()
// Read the response body
rspBytes, err := io.ReadAll(rsp.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("error reading response: %v", err)
}
// Print the response body
fmt.Printf("%s\n", string(rspBytes))
}
Now, trying the mTLS server with:
go run client-mtls.go --url https://localhost:8889/hello-world.txt --cert certs/client.crt --key certs/client.key
Returns the expected result:
mTLS Hello World!
However, we pass the client certificate and key as command-line arguments. In a real-world scenario, we want to use the system keystore to manage the client certificate and key.
Using a custom signer for the mTLS client certificate
The following article will cover creating a custom Go signer for the mTLS client certificate. This work will pave the way for us to use the system keystore to manage the client certificate and key.
Example code on GitHub
The example code is available on GitHub at https://github.com/getvictor/mtls/tree/master/mtls-with-go
mTLS Go client video
Note: If you want to comment on this article, please do so on the YouTube video.